Home
- Home
- Blog
Author :
Global TechHub
Introduction
If
you're looking for MuleSoft Interview Questions for Experienced & Freshers,
you are at right place. There are lot of opportunities from many reputed
companies in the world. According to research MuleSoft has a market share of
about 5.9%. So, You still have opportunity to move ahead in your career in Mule
ESB. There are different positions open as Mule ESB Developer, Mule ESB
architect, Mule ESB engineer, Mule ESB consultant, Mule ESB expert, etc across
many top IT hubs.
Overview
What is ESB?
An
enterprise service bus (ESB) is software architecture for middleware that
provides fundamental services for more complex architectures. For example, an
ESB incorporates the features required to implement a service-oriented
architecture (SOA). In a general sense, an ESB can be thought of as a mechanism
that manages access to applications and services (especially legacy versions) to
present a single, simple, and consistent interface to end-users via Web- or
forms-based client-side front ends.
What Is Mule ESB?
Mule is
a lightweight event-driven enterprise service bus (ESB) and an integration
platform. It is a lightweight and modular solution that could scale from an
application-level messaging framework to an enterprise-wide highly
distributable object broker.
What are the features of Mule ESB/ESB
?
Transport: applications can accept input from a
variety of means, from the file system to the network.
Data format: speaking the right protocol is only
part of the solution, as applications can use almost any form of representation
for the data they exchange.
Invocation styles: synchronous, asynchronous, or batch
call semantics entail very different integration strategies.
Lifecycles: applications of different origins
that serve varied purposes tend to have disparate development, maintenance, and
operational lifecycles.
Why Mule Was Designed ?
Mule’s
core was designed as an event-driven framework combined with a unified
representation of messages, expandable with pluggable modules. These modules
would provide support for a wide range of transports or add extra features,
such as distributed transactions, security, or management. Mule was also designed
as a programmatic framework offering programmers the means to graft additional
behavior such as specific message processing or custom data transformation.
What Are Differences Between Mule And
Other Commercial Esbs ?
Prescriptive
deployment model, whereas Mule supports a wide variety of deployment
strategies. Prescriptive SOA methodology, whereas Mule can embrace the
architectural style and SOA practices in place where it is deployed. Mainly
focused on higher-level concerns, whereas Mule deals extensively with all the
details of integration. Strict full-stack web service orientation, whereas
Mule’s capacities as an integration framework open it to all sorts of other
protocols. Comprehensive documentation, a subject on which MuleSource has made
huge progress recently.
What Is Model Layer In Mule ?
The
first logical layer is the model layer. A Mule model represents the runtime
environment that hosts services. It defines the behavior of Mule when
processing requests handled by services. The model provides services with
supporting features, such as exception strategies. It also provides services
with default values that simplify their configuration.
What Is Service Layer In Mule ?
A Mule
service is composed of all the Mule entities involved in processing particular
requests in predefined manners.A service is defined by a specific
configuration. This configuration determines the different elements, from the
different layers of responsibility, that will be mobilized to process the
requests that it will be open to receive. Depending on the type of input
channel it uses, a service may or may not be publicly accessible outside of the
ESB.
What Is Transport Layer In Mule ?
The
transport layer is in charge of receiving or sending messages. This is why it
is involved with both inbound and outbound communications. A transport
manifests itself in the configuration by the following elements: connectors,
endpoints and transformers.
A
transport also defines one message adapter. A message adapter is responsible
for extracting all the information available in a particular request (data,
meta information, attachments, and so on) and storing them in
transport-agnostic fashion in a Mule message.
What Is Connector In Mule ?
A
connector is in charge of controlling the usage of a particular protocol. It is
configured with parameters that are specific to this protocol and holds any
state that can be shared with the underlying entities in charge of the actual
communications.
For
example: a JMS connector is configured with a Connection, which is shared by
the different entities in charge of the actual communication.
What Is Endpoint In Mule ?
An
endpoint represents the specific usage of a protocol, whether it is for
listening/polling, reading from, or writing to a particular target destination.
Hence it controls what underlying entities will be used with the connector they
depend on. The target destination itself is defined as a URI. Depending on the
connector, the URI will bear a different meaning; for example, it can represent
a URL or a JMS destination.
What Is Transformer In Mule ?
A
transformer takes care of translating the content of a message from one form to
another. It is possible to chain transformers to cumulate their effects.
Transformers can kick in at different stages while a message transits through a
service.
What Is Router In Mule ?
Routers
play a crucial role in controlling the trajectory a message will follow when it
transits in Mule. They are the gatekeepers of the endpoints of a service,
taking care of keeping messages on the right succession of tracks so they can
reach their intended destinations. Certain routers act like the big
classification yards: they can split, sort, or regroup messages based on
certain conditions.
What Is Filter In Mule ?
Filters
are a powerful complement to the routers. Filters provide the brains routers
need to make smart decisions about what to do with messages in transit. Some
filters go as far as deeply analyzing the content of a message for a particular
value on which their outcome will be based.
What Is Component In Mule ?
Components
are the centerpiece of Mule’s services. Each service is organized with a
component at its core and inbound and outbound routers around it. Components
are used to implement a specific behavior in a service. This behavior can be as
simple as logging messages or can go as far as invoking other services.
Components can also have no behavior at all; in that case they are pass-through
and make the service act as a bridge between its inbound and outbound routers.
How Message In Mule Is Composed ?
Ø A Mule message is composed of
different parts: The payload, which is the main data content carried by the
message.
Ø
The
properties, which contain the meta information much like the header of a SOAP
envelope or the properties of a JMS message. Optionally, multiple named
attachments, to support the notion of multipart messages.
Ø Optionally, an exception payload,
which holds any error that occurred during the processing of the event.
What Are Configuration Builders In Mule
?
Mule
uses configuration builders that can translate a human-authored configuration
file into the complex graph of objects that constitutes a running node of this
ESB. The main builders are of two kinds: a Spring-driven builder, which works
with XML files, and a script builder, which can accept scripting language
files.
Why Spring-driven Configuration
Builder Is Important Than Script Builder ?
The
advantages of Spring-driven configuration builder
Ø It is the most popular — you are more
likely to find examples using this syntax.
Ø
It
is the most user friendly — Spring takes care of wiring together all the moving
parts of the ESB, something you must do by hand with a script builder.
Ø It is the most expressive — dedicated
XML schemas define the domain-specific language of Mule, allowing you to handle
higher-level concepts than the scripting approach does.
What Is Bridge Component In Mule ?
A bridge
component is used to pass the messages from the inbound router to the outbound
one. A bridge is a neutral component: it does not perform any action or modify
messages that it processes.
What Tags Are Used To Configure
Spring Elements In Mule ?
Tags
like <spring:bean/> <spring:entry/> etc. are used to configure
spring stuff.
What Are Available Approaches Used
For Modularizing Configurations In Mule ?
There
are different following approaches that can be used when modularizing a
configuration.
Independent configurations – a Mule instance can load several
independent configuration files side by side.
Inherited configurations – main idea is to express a formal
parent-child dependency between two configurations. By strongly expressing this
dependency, you will have the guarantee at boot time that no configuration file
has been omitted. Simply by using the same name for the parent and child models
and by flagging the child as being an heir, as shown here:
<model
name="myConfig">
<model
name="myConfig" inherit="true">
Imported configurations – You can easily import external
Spring application context files into your Mule configuration files. The
following illustrates how instance.xml would import its Spring context file:
<spring:beans>
<spring:import
resource="instance-beans.xml" />
</spring:beans>
Heterogeneous configurations – It is possible to mix several
styles of Mule configuration in an instance. An instance can be configured with
a Groovy script and Spring XML configuration builders.
Give An Example Of Stdio Connector In
Mule ?
<stdio:connector
name="SystemStreamConnector" promptMessage="Please enter
something: " messageDelayTime="1000"/>
Give An Example Of Http Connector In
Mule ?
<http:connector
name="HttpConnector"proxyHostname="proxyHostname"
proxyPort="proxyPort"
proxyUsername="proxyUsername"proxyPassword="proxyPassword"/>
When Does Mule Instantiates A
Connector ?
If Mule
figures out that one of our endpoints needs a particular connector, it will
automatically instantiate one for us, using all the default values for its
different configuration parameters. This is a perfectly viable approach if we
are satisfied with the behavior of the connector when it uses its default
configuration. This is often the case for the VM or HTTP transports.
What Is Transport Service Descriptor
In Mule ?
The
connector has a technical configuration known as the Transport Service Descriptor
(TSD). This hidden configuration is automatically used for each instance of the
connector. It defines technical parameters such as what classes to use for the
message receivers, requesters, and dispatchers; or the default transformers to
use in inbound, outbound, and response routers. Knowing these default values is
essential to grasping the behavior of a transport.
How Many Endpoints Are There In Mule
?
There
are two endpoints :
Ø Inbound
Ø Outbound.
You will
use inbound and outbound endpoints to communicate between components and
services inside Mule as well as with the outside world.
What Is An Outbound Endpoint In Mule
?
Outbound
endpoints are used to send data. An outbound endpoint is used to do things such
as send SOAP messages, write to file streams, and send email messages.
What Is Global Endpoint In Mule ?
An
endpoint destination that is shared by several routers, it is worth creating a
global endpoint. A global endpoint is not typified for inbound or outbound
routing, making it usable in many different places in a configuration file. It
must be named so it can actually be used in a service, which will reference the
global endpoint by its name. A global endpoint can also help clarify the usage
of a particular destination.
Why Does An Endpoint In Mule Offer An
Address Attribute ?
This
allows us to configure a generic endpoint using the Mule 1.x style of URI-based
destination addresses instead of the dedicated attributes of the specific
endpoint element.
Give An Example Of File Endpoint In
Mule ?
<file:endpoint
name="tmpPoller" path="/tmp"
fileAge="1000"pollingFrequency="2000"/>
What Is Streaming Property In File
Connector In Mule ?
The
value of this streaming property can be either true or false. If it is set to
true then we are actually working on stream of file data otherwise we are
working with file itself.
What Is Pollingfrequency Property In
File Connector In Mule ?
When we
want file inbound endpoints to poll their source directories for new content.
This is accomplished by setting the pollingFrequency to some milliseconds
value.
What Is Autodelete Property In File
Connector In Mule ?
The
default value of autoDelete is true. Therefore, a file inbound endpoint will,
by default, remove the file from the source directory once it is read by the
inbound endpoint. If you do not want to delete file automatically then you can
set autoDelete property to false.
What Is Fileage Property In File
Connector In Mule ?
The
fileAge property specifies how long the endpoint should wait before reading the
file again. For instance, a fileAge of 60000 indicates Mule should wait a
minute before processing the file again.
How To Send Only Certain Types Of
File From One Directory To Another In Mule ?
Use the
below element in file inbound to filter certain types of files.
<file:filename-wildcard-filter
pattern="file*.xml"/></file:inbound-endpoint>
pattern
indicates what pattern of file names should move from one directory to another
directory.
What Is Vm Transport In Mule ?
The VM
transport is a special kind of transport that you’ll use to send messages via
memory. These messages never leave the JVM the Mule instance is running in.
What Is Multicasting Router In Mule ?
The
multicasting router can send messages to multiple endpoints over different
transports. The multicasting router allows you to easily move the same messages
across these different endpoints.
What Is Mule Transformer ?
It is an
event, more specifically an instance of org.mule.api.MuleEvent. This object
carries not only the actual content of the message but also the context of the
event.
What Is Mule Context ?
The Mule
context is composed of references to different objects, including security
credentials, if any, the session in which the request is processed. All
internals of the ESB are accessible through Mule context
What Is Payload In Mule ?
The
content of a message, also known as payload. It is wrapped in an instance of
org.mule.api.MuleMessage, which provides different means of accessing the
payload under different forms. A MuleMessage also contains properties, much
like the header of a SOAP envelope or the properties of a JMS message, and can
also have multiple named attachments.
What Are Different Type Of Messages
In Mule ?
Ø
Bridge messages: Pass messages from inbound to
outbound routers.
Ø
Echo and log messages: Log messages and move them from
inbound to outbound routers.
Ø
Build messages: Create messages from fixed or
dynamic values
Why Mule Esb?
Mule ESB
is lightweight but highly scalable, allowing you to start small and connect
more applications over time. Mule manages all the interactions between
applications and components transparently, regardless of whether they exist in
the same virtual machine or over the Internet, and regardless of the underlying
transport protocol used.
There
are currently several commercial ESB implementations on the market. However,
many of these provide limited functionality or are built on top of an existing
application server or messaging server, locking you into that specific vendor.
Mule is vendor-neutral, so different vendor implementations can plug in to it.
You are never locked in to a specific vendor when you use Mule.
What are Batch Jobs in Mule ESB ?
A batch
job is a top-level element in Mule which exists outside all Mule flows. Batch
jobs split large messages into records which Mule processes asynchronously in a
batch job; just as flows process messages, batch jobs process records.
A batch
job contains one or more batch steps which, in turn, contain any number of
message processors that act upon records as they move through the batch job.
During batch processing, you can use record-level variables (recordVars) and
MEL expressions to enrich, route or otherwise act upon records.
What are the different types of Flow
Processing Strategies ?
There
are six different types of Flow Processing Strategies. They are
Ø Asynchronous Flow Processing
Strategy.
Ø
Custom
Processing Strategy.
Ø
Thread
Per Processing Strategy.
Ø
Queued
Asynchronous Flow Processing Strategy.
Ø
Synchronous
Flow Processing Strategy.
Ø
Non-blocking
Flow Processing Strategy.
Ø Queued Flow Processing Strategy.
Why the Mulesoft is preferred than
other ESB implementations ?
Mule is
lightweight but highly scalable, allowing you to start small and connect more
applications over time. The ESB manages all the interactions between applications
and components transparently, regardless of whether they exist in the same
virtual machine or over the Internet, and regardless of the underlying
transport protocol used.
Several
commercial ESB implementation provide limited functionality or built on top of
an existing application server or messaging server, locking you into that
specific vendor. Mule is vendor-neutral, so different vendor implementations
can plug in to it. You are never locked in to a specific vendor when you use
Mule.
What Is Filter In Mule ?
Filters
are a powerful complement to the routers. Filters provide the brains routers
need to make smart decisions about what to do with messages in transit. Some
filters go as far as deeply analyzing the content of a message for a particular
value on which their outcome will be based.
What are the different types of Web
services ?
There
are mainly two types of web services.
Ø
SOAP
web services.
Ø
RESTful
web services.
How to add classes/jars to the Mule
class path ?
Use the
MULE_LIB variable (generally set in the run script)
To
include JAR file(s) in a mule class path, declare each dependent jar file in
the MULE_LIB entry.
For
spring resource, if the XML bean declaration is placed within a project,
include the project JAR file in the class path too (i.e., if not included, Mule
will throw a **.xml not found on class path)
What is Mule Data Integrator ?
Mule has
released a data integrator tool, it is a visual mapping tool which supports
flat file, java object, XML mappings, etc. Coding complex mappings can be very
tedious and additionally difficult to maintain, the mule data integrator with
drag and drop facilities makes building and maintaining mappings very simple.
The
mapping is done in eclipse (plugins required) and executed on a data integrator
runtime which sits on top of Mule ESB – this requires a license.
Where to find the class Abstract Mule
TestCase ?
This is
in 1.4/1.4.1 distributions but was missing from the 1.3.3 distribution – the
class is defined in /lib/mule/mule-core-.jar.
Our design
of course tutorials and interview questions is practical and informative. At
TekSlate, we offer resources to help you learn various IT courses. We avail
both written material and demo video tutorials. For in-depth knowledge and
practical experience explore.
Mule won’t start? Check your
Environment ?
The java
and mule environment variables must be setup correctly for mule to start. If
you are experiencing problems check the following variables:
MULE_HOME
– should be the location of the mule install
JAVA_HOME
– should be the location of the JDK
PATH –
should have both JAVA_HOME\bin and MULE_HOME\bin in the path.
Check
all of the above carefully. Some systems with multiple JDK’s installed can end
up with incorrect mappings between the PATH and the JAVA_HOME, which will stop
mule from loading.
What are Web Services ?
Web
service is a functionality or a small piece of program in any programming
language that can be accessed over HTTP. Message format can be XML or JSON or
any other program as long as the other programs can understand and communicate.
A Web
service can be of synchronous or asynchronous type. Any web service has a
server-client relationship and it can have multiple clients.
How can we create and consume SOAP
service in Mule ?
Creating SOAP Service – We can create a SOAP service same
as we create Mule Project With RAML, the only change is instead of RAML we need
to import Concert WSDL.
Consuming SOAP Service – We can use Web Service Consumer or
CXF component in our mule flow to access/consume SOAP service.
The different types of variables in
Mule ESB are:
Ø
Flow
Variable
Ø
Session
Variable
Ø
Record
Variable
What are the various types of
Exception Handling in Mule ESB ?
The
types of exception handling in Mule ESB are:
Ø
Default
Exception Handling
Ø
Global
Exception Handling
Ø
Catch
Exception Handling
Ø Choice Exception Handling
What are the Features of Mule ESB ?
An ESB
is a used for integration using a service-oriented approach. Its main features
are:
Ø
Set
of Service Container
Ø
Message
Transformation Service
Ø
Message
Routing Service
Ø Web Service Security
What is the difference between SOAP
and REST ?
SOAP
-> REST
ü
SOAP
is a protocol. -> REST is an architectural style.
ü
SOAP
stands for Simple Object Access Protocol. -> REST stands for
REpresentational State Transfer.
ü
SOAP
can’t use REST because it is a protocol. -> REST can use SOAP web services
because it is a concept and can use any protocol like HTTP, SOAP.
ü
SOAP
uses services interfaces to expose the business logic. -> REST uses URI to
expose business logic.
ü
SOAP
defines standards to be strictly followed. -> REST does not define too much
standards like SOAP.
ü
SOAP
defines standards to be strictly followed. -> REST does not define too much
standards like SOAP.
ü
SOAP
requires more bandwidth and resource than REST. -> REST requires less
bandwidth and resource than SOAP.
ü
SOAP
defines its own security. -> RESTful web services inherit security measures
from the underlying transport.
ü
SOAP
permits XML data format only. -> REST permits different data format such as
Plain text, HTML, XML, JSON etc.
ü
SOAP
is less preferred than REST. -> REST more preferred than SOAP.
What is Shared Resource in Mule and
how they have been used?
We can
make connectors as an reusable component by defining them as common resources
and expose them to all applications deployed under a same domain, these
resources are known as shared resources. These shared resource needs to be
defined inside Mule Domain Project and then referred to each of the projects
that are meant to use the elements in it.
What are the different ESBs in the
market?
There
are various ESB's available in the market. Some are opensource, some licenced:
Ø
Talend
Ø
Mule
ESB
Ø
JBoss
Fuse ESB
Ø
IBM
WESB
Ø
Opensource
ESB
Ø
WSO2
Explain
ESB Integration core principles?
Transformation - Data transformation between
canonical data formats and specific data formats required by each ESB
connector.
Transportation - Transport protocol negotiation
between multiple formats. Such as HTTP, JMS, JDBC.
Mediation - Providing multiple interfaces for
the purpose of a) supporting multiple versions of a service for backwards
compatibility or alternatively, b) to allow for multiple channels to the same
underlying component implementation. This second requirement may involve
providing multiple interfaces to the same component, one legacy interface (flat
file) and one standards compliant (SOAP/XML) interface.
Non-functional consistency - For a typical ESB initiative, this
can include consistency around the way security and monitoring policies are
applied and implemented.
How to select an ESB?
Usability: How complicated is the installation
process? The learning curve of the ESB should not be long.
Maintainability: How to monitor the product? If any
GUI terminal is available for monitoring the services.
Community: Is there active community for the
ESB. Various discussion forums, tutorials etc.
Enterprose Support- Is the product support reliable.
What services are available.
Flexibility: Can the ESB be configured to meet
the business requirements.
Reliability: The reliablity of the ESB. Its
current users and various case studies if available.
Cost: The cost of the ESB. Its Licence
policies. Support cose. etc.
What are the advantages of using an
ESB?
Provides
a way for end points to connect to each other without having to directly talk
to each other. It simplifies the communications for the end points as they only
have to conform to a standard communication interface, the bus.
An ESB
provides a single place to get some key end point metrics: frequency,
availability, and performance.
An ESB
tends to provide more than one communication interface. However, a developer
only needs to choose the easiest one to get and receive the data from the bus.
What is REST?
REST
stands for Representaional State Transfer or RESTful web service. REST is a
client-server architecture which means each unique URL is representation of
some object or resource. Any REST API developed uses HTTP methods explicitly
and in a way that’s consistent with the protocol definition. This basic REST
design principle establishes a one-to-one mapping between create, read, update,
and delete (CRUD) operations and HTTP methods. According to this mapping:
Ø
To
create a resource on the server, use POST.
Ø
To
retrieve a resource, use GET.
Ø
To
change the state of a resource or to update it, use PUT.
Ø
To
remove or delete a resource, use DELETE.
What is RAML and why we use it?
RAML –
REST ful API Modeling Language
RAML is
similar to WSDL, it contains endpoint URL, request/response schema, HTTP
methods and query and URI parameter.
RAML
helps client (a consumer of the service) know, what the service is and what/how
all operations can be invoked.
RAML
helps the developer in creating the initial structure of this API. RAML can
also be used for documentation purpose.
What are the Message Sources in Mule
ESB?
Message
sources in Mule are usually Anypoint Connectors, elements which provide connectivity
to a specific external source, either via a standard protocol (such as HTTP,
FTP, SMTP) or a third-party API (such as Salesforce.com, Twitter, or MongoDB).
What is the difference between ESB
and JMS?
ESB
provides the middleware and interfaces that allow businesses to connect their
applications without writing code.
JMS
provides messaging capability and facilitates communication between the
modules/applications.
Download
|
S. No
|
File Name
|
Size
|
Download
|
|
1
|
Mulesoft
ESB Interview Questions & Answers.pdf
|
1.0 MB
|

 Global TechHub
Global TechHub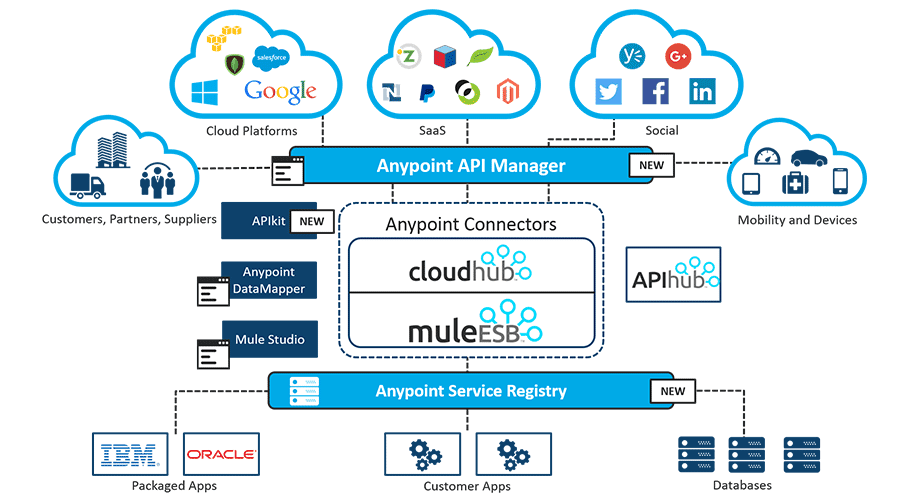
Comments
Post a Comment